量子ニューラルネットワークの最初のステップ
バックプロパゲーションを手作業で実装します
実装(DescentGradient.ipynb)
インポート
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline機能の実装
def plotCost(result, title = 'Cost x Epochs', show = True):
plt.plot(result, color='r')
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Cost (J)')
if show:
plt.show()
def plotData(x, y, title = 'Plot Data', show = True):
plt.plot(X, y, 'ro', ms=10, mec='k')
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
if show:
plt.show()
def plotCurve(x, y, label = 'Hypothesis', show = True):
plt.plot(X, y, color='blue', label=label)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
if show == True:
plt.show()
def plotNorm(grad, label = 'Gradient Norm', show = True):
norm = np.linalg.norm(grad, axis=1)
idxs = [i for i in range(len(norm))]
plt.scatter(idxs, norm, color = 'k', label=label)
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
if show == True:
plt.show()
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))テストデータの作成
X_test = np.array([1, 2, 3])
y_test = np.array([3.0, 5.0, 7.0])
w_test = np.array([0.3123739, 0.99869863, 0.19889807])リグレッサーの実装
class RegressorLinear():
def hypothesis(self, X, theta):
if X.ndim == 0:
X = np.array([X])
y = theta[0] + theta[1]*X
return y
def gradient(self, X, y, theta):
m = y.size
n = theta.shape[0]
grad = np.zeros(n)
if X.ndim == 0:
X = np.array([X])
if y.ndim == 0:
y = np.array([y])
for i in range(m):
x = X[i]
diff = self.hypothesis(x, theta) - y[i]
grad[0] += diff * 1
grad[1] += diff * x
grad = (1 / m) * grad
return grad
class RegressorSquare():
def hypothesis(self, X, theta):
if X.ndim == 0:
X = np.array([X])
y = theta[0] + theta[1]*X + theta[2]*(X**2)
return y
def gradient(self, X, y, theta):
m = y.size
n = theta.shape[0]
grad = np.zeros(n)
if X.ndim == 0:
X = np.array([X])
if y.ndim == 0:
y = np.array([y])
for i in range(m):
x = X[i]
diff = self.hypothesis(x, theta) - y[i]
grad[0] += diff * 1
grad[1] += diff * x
grad[2] += diff * x**2
grad = (1 / m) * grad
return grad
class RegressorNonLinear():
def hypothesis(self, X, theta):
if X.ndim == 0:
X = np.array([X])
y = theta[0] + theta[1]*X + theta[2]*(X**2) + theta[3]*np.exp(theta[4]*X) + theta[5]*np.log(theta[6]*X) + theta[7]*np.cos(theta[8]*X) + theta[9]*np.sin(theta[10]*X)
return y
def gradient(self, X, y, theta):
m = y.size
n = theta.shape[0]
grad = np.zeros(n)
if X.ndim == 0:
X = np.array([X])
if y.ndim == 0:
y = np.array([y])
for i in range(m):
x = X[i]
diff = self.hypothesis(x, theta) - y[i]
grad[0] += diff * 1
grad[1] += diff * x
grad[2] += diff * (x**2)
grad[3] += diff * np.exp(theta[4] * x)
grad[4] += diff * theta[3] * np.exp(theta[4] * x) * x
grad[5] += diff * np.log(theta[6] * x)
grad[6] += diff * (theta[5] / theta[6])
grad[7] += diff * np.cos(theta[8] * x)
grad[8] += diff * (-theta[7] * np.sin(theta[8]*x) * x)
grad[9] += diff * np.sin(theta[10] * x)
grad[10] += diff * theta[9] * np.cos(theta[10]*x) * x
grad = (1 / m) * grad
return grad
class RegressorTest():
def hypothesis(self, X, theta):
print('テスト回帰器の目的関数を呼び出す')
return 0
def gradient(self, X, y, theta):
print('回帰テストの勾配ベクトルを呼び出す')
return np.zeros(theta.shape[0])
def costFunction(X, y, theta, regressor):
m = X.shape[0]
h = regressor.hypothesis(X, theta)
J = (1/(2 * m)) * np.sum((h - y)**2)
return J
J_test = costFunction(X_test, y_test, w_test, regressor=RegressorTest())
print("予想されるターゲットとのテスト")
print("期待される結果: 13.833333333333332")
print("受信結果:", J_test)テスト回帰器の目的関数を呼び出す
予想されるターゲットとのテスト
期待される結果: 13.833333333333332
受信結果: 13.833333333333332
勾配アルゴリズムの実装
def gradientDescent(X, y, initial_theta, regressor, learning_rate = 0.001, iterations = 100):
theta = initial_theta.copy()
J_history = np.zeros(iterations)
grad_history = []
grad = 0
for i in range(iterations):
J = costFunction(X, y, theta, regressor)
grad = regressor.gradient(X, y, theta)
theta = theta - (learning_rate * grad)
J_history[i] = J
grad_history.append(grad)
return theta, J_history, grad_history
gradient_test = gradientDescent(X_test, y_test, w_test, regressor=RegressorSquare())
plotCost(gradient_test[1])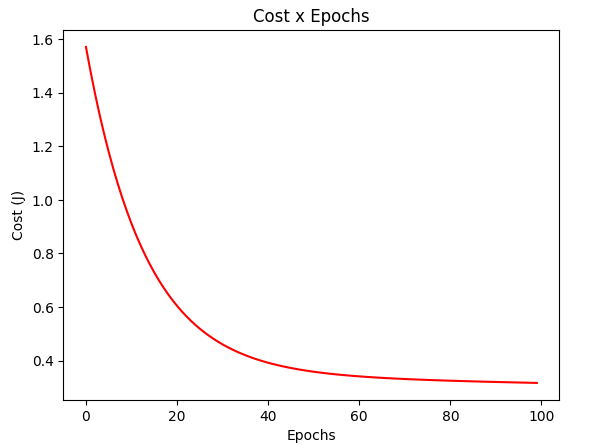
def gradientDescentMiniBatch(X, y, initial_theta, regressor, learning_rate = 0.001, iterations = 100, batch_size = 32):
X = X.copy()
y = y.copy()
theta = initial_theta.copy()
J_history = np.zeros(iterations)
grad_history = []
grad = 0
m = X.shape[0]
for i in range(iterations):
indices = np.random.permutation(m)
X = X[indices]
y = y[indices]
J = costFunction(X, y, theta, regressor)
for k in range(0, m, batch_size):
grad = regressor.gradient(X[k:k+batch_size], y[k:k+batch_size], theta)
theta = theta - (learning_rate * grad)
J_history[i] = J
grad_history.append(grad)
return theta, J_history, grad_history
gradient_test = gradientDescentMiniBatch(X_test, y_test, w_test, batch_size = 1, regressor=RegressorSquare())
plotCost(gradient_test[1])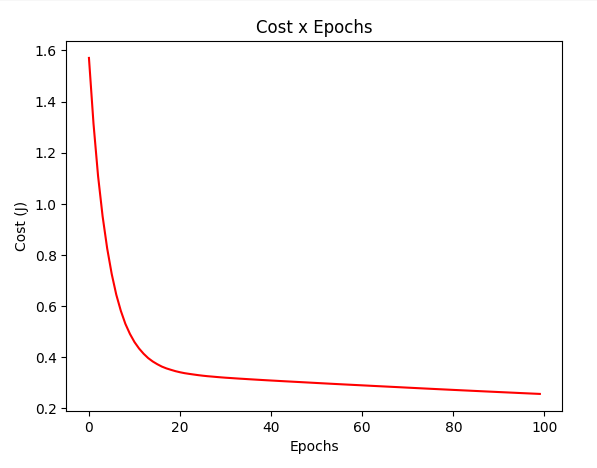
def gradientDescentStochastic(X, y, initial_theta, regressor, learning_rate = 0.001, iterations = 100):
X = X.copy()
y = y.copy()
theta = initial_theta.copy()
J_history = np.zeros(iterations)
grad_history = []
grad = 0
m = X.shape[0]
for i in range(iterations):
indices = np.random.permutation(m)
X = X[indices]
y = y[indices]
J = costFunction(X, y, theta, regressor)
for k in range(len(X)):
grad = regressor.gradient(X[k], y[k], theta)
theta = theta - (learning_rate * grad)
J_history[i] = J
grad_history.append(grad)
return theta, J_history, grad_history
gradient_test = gradientDescentStochastic(X_test, y_test, w_test, regressor=RegressorSquare())
plotCost(gradient_test[1])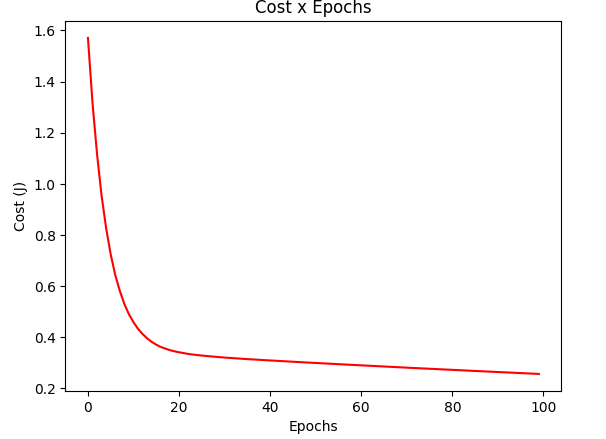
def gradientDescentMomentum(X, y, initial_theta, regressor, learning_rate = 0.001, iterations = 100, batch_size = 32, momentum_rate = 0.9):
X = X.copy()
y = y.copy()
theta = initial_theta.copy()
J_history = np.zeros(iterations)
grad_history = []
grad = 0
m = X.shape[0]
momentum = np.zeros(theta.shape[0])
for i in range(iterations):
indices = np.random.permutation(m)
X = X[indices]
y = y[indices]
J = costFunction(X, y, theta, regressor)
for k in range(0, m, batch_size):
grad = regressor.gradient(X[k:k+batch_size], y[k:k+batch_size], theta)
momentum = momentum_rate * momentum + (1 - momentum_rate) * grad
theta = theta - (learning_rate * momentum)
J_history[i] = J
grad_history.append(grad)
return theta, J_history, grad_history
gradient_test = gradientDescentMomentum(X_test, y_test, w_test, regressor=RegressorSquare(), batch_size = 1)
plotCost(gradient_test[1])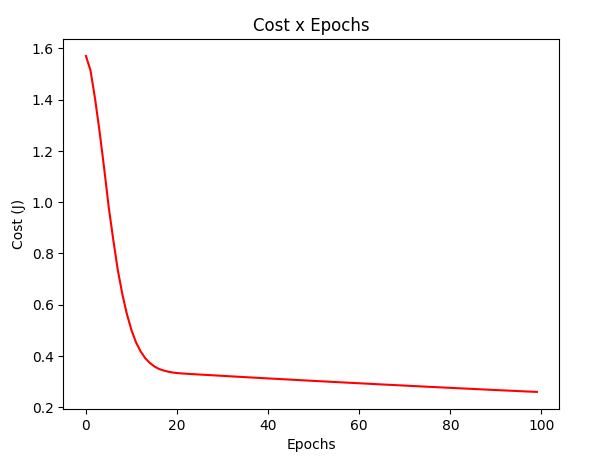
def gradientDescentAdaGrad(X, y, initial_theta, regressor, learning_rate = 0.001, iterations = 100, eps=0.0000001):
X = X.copy()
y = y.copy()
theta = initial_theta.copy()
J_history = np.zeros(iterations)
grad_history = []
grad = 0
sum_gradient_squared = 0
for i in range(iterations):
indices = np.random.permutation(X.shape[0])
X = X[indices]
y = y[indices]
J = costFunction(X, y, theta, regressor)
for k in range(len(X)):
grad = regressor.gradient(X[k], y[k], theta)
sum_gradient_squared += (grad)**2
theta = theta - (learning_rate * grad / (sum_gradient_squared + eps)**(1/2))
J_history[i] = J
grad_history.append(grad)
return theta, J_history, grad_history
gradient_test = gradientDescentAdaGrad(X_test, y_test, w_test, regressor=RegressorSquare())
plotCost(gradient_test[1])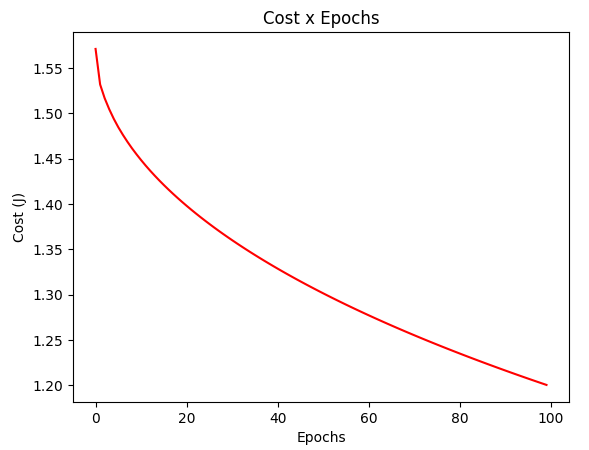
データの読み込み
合成データベースの生成
def generateDataset():
np.random.seed(3)
n = 100
data1_x = np.zeros(n)
data1_y = np.zeros(n)
for i in range(0,n):
data1_x[i] = (i + 3*(np.random.random() - 0.5))/(n/5)
data1_y[i] = data1_x[i]**2 - 2*data1_x[i]*(0.5*(np.random.random() - 0.5)) + 3*np.cos(data1_x[i] + (np.random.random() - 0.5))
return data1_x, data1_y初期ウェイトの生成
np.random.seed(3)
initial_theta_r12 = np.array([np.random.random() for _ in range(12)])データセットと開始重みの選択
X, y = generateDataset()
initial_theta = initial_theta_r12[0:11]
print('データセットの寸法:', X.shape)
print('初期ウェイト:', initial_theta)データセットの寸法: (100,)
初期ウェイト: [0.5507979 0.70814782 0.29090474 0.51082761 0.89294695 0.89629309 0.12558531 0.20724288 0.0514672 0.44080984 0.02987621]
トレーニングのパラメータ化
訓練アルゴリズムの実行における将来の比較を容易にするための共通の実行パラメータの定義
DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE = 0.001
DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS = 100
DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE = 32
DEFAULT_MOMENTUM_RATE = 0.9
DEFAULT_ADAGRAD_EPS = 0.0000001
DEFAULT_REGRESSOR = RegressorSquare()モデルトレーニング
バッチ降順勾配
resultClassic = gradientDescent(X, y, initial_theta, regressor = DEFAULT_REGRESSOR, learning_rate=DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, iterations=DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS)
plotCost(resultClassic[1])
plotData(X, y, show = False)
plotCurve(X, DEFAULT_REGRESSOR.hypothesis(X, resultClassic[0]))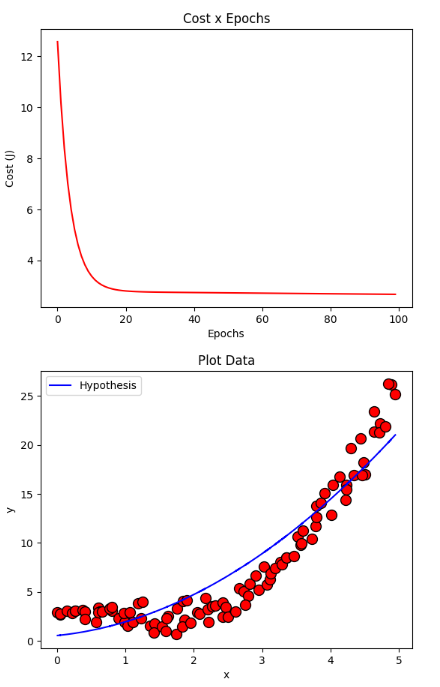
ミニバッチの降下勾配
resultMiniBatch = gradientDescentMiniBatch(X, y, initial_theta, regressor = DEFAULT_REGRESSOR, learning_rate=DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, iterations=DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS, batch_size=DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE)
plotCost(resultMiniBatch[1])
plotData(X, y, show = False)
plotCurve(X, DEFAULT_REGRESSOR.hypothesis(X, resultMiniBatch[0]))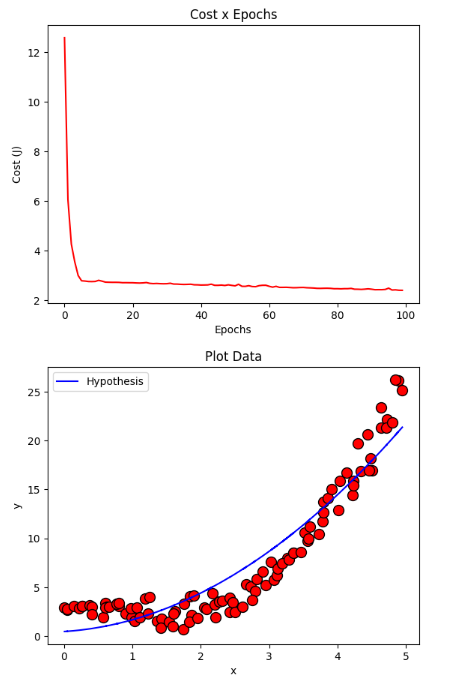
確率的に下降する勾配
resultStochastic = gradientDescentStochastic(X, y, initial_theta, regressor = DEFAULT_REGRESSOR, learning_rate=DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, iterations=DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS)
plotCost(resultStochastic[1])
plotData(X, y, show = False)
plotCurve(X, DEFAULT_REGRESSOR.hypothesis(X, resultStochastic[0]))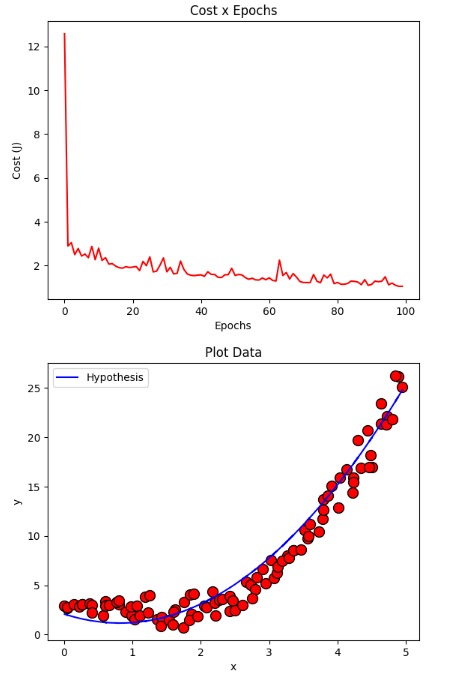
モメンタムによる勾配降下
resultMomentum = gradientDescentMomentum(X, y, initial_theta, regressor = DEFAULT_REGRESSOR, learning_rate=DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, iterations=DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS, batch_size=DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE, momentum_rate=DEFAULT_MOMENTUM_RATE)
plotCost(resultMomentum[1])
plotData(X, y, show = False)
plotCurve(X, DEFAULT_REGRESSOR.hypothesis(X, resultMomentum[0]))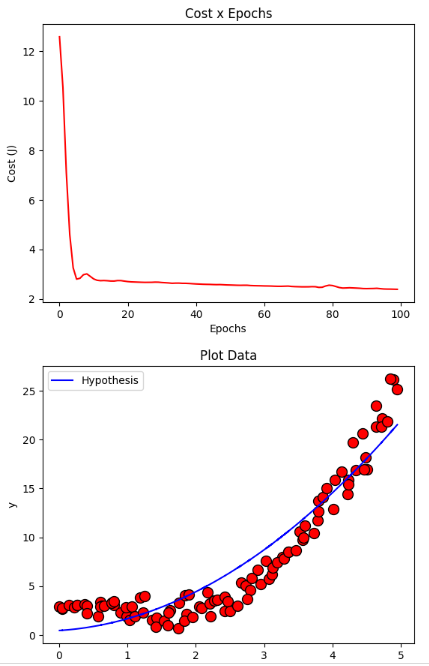
下降グラディエント AdaGrad
resultAdaGrad = gradientDescentAdaGrad(X, y, initial_theta, regressor = DEFAULT_REGRESSOR, learning_rate=DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, iterations=DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS, eps=DEFAULT_ADAGRAD_EPS)
plotCost(resultAdaGrad[1])
plotData(X, y, show = False)
plotCurve(X, DEFAULT_REGRESSOR.hypothesis(X, resultAdaGrad[0]))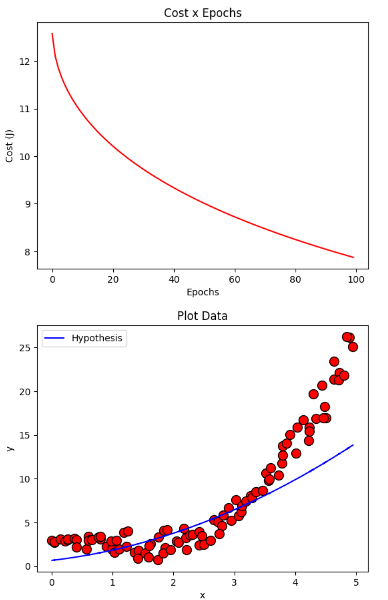
分析
結果のグループ化
results = [('classic', resultClassic), ('stochastic', resultStochastic), ('minibatch', resultMiniBatch), ('momentum', resultMomentum), ('adagrad', resultAdaGrad) ]比較コスト関数(J)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(results), figsize=(30, 4), sharex=True, sharey=True)
parameters = '(learningRate:{}, epochs:{}, batchSize:{}, momentum:{}, adagradEPS:{})'.format(DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS, DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE, DEFAULT_MOMENTUM_RATE, DEFAULT_ADAGRAD_EPS)
suptitle = '下降勾配の変化の比較 {}'.format(parameters)
fig.suptitle(suptitle, fontsize=14, y=1.05)
for i, ax in enumerate(axes):
name, result = results[i]
ax.set_title(name)
ax.set_xlabel('epochs')
ax.set_ylabel('cost(j)')
if result != None:
ax.plot(result[1], color = 'r')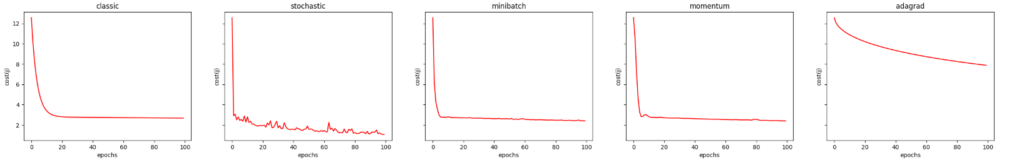
学習した目的関数の比較
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, len(results), figsize=(30, 4))
parameters = '(learningRate:{}, epochs:{}, batchSize:{}, momentum:{}, adagradEPS:{})'.format(DEFAULT_LEARNING_RATE, DEFAULT_NUMBER_EPOCHS, DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE, DEFAULT_MOMENTUM_RATE, DEFAULT_ADAGRAD_EPS)
suptitle = '下降勾配の変化の比較 {}'.format(parameters)
fig.suptitle(suptitle, fontsize=14, y=1.05)
for i, ax in enumerate(axes):
name, result = results[i]
ax.set_title(name)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
if result != None:
ax.scatter(X, y, color = 'r', marker = 'o', s = 100, edgecolors = 'k')
ax.plot(X, DEFAULT_REGRESSOR.hypothesis(X, result[0]), color = 'b', label = 'Hypothesis')
ax.legend()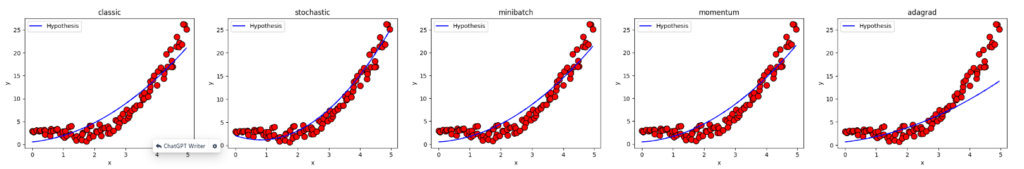
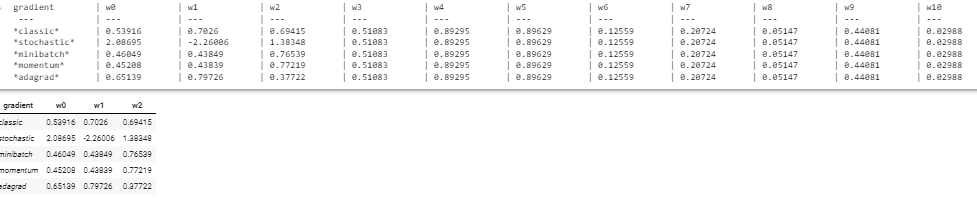
学習したウェイトのリスト
header = 'gradient'
sep = ' --- '
for i in range(len(initial_theta)):
header += ' \t| w{} '.format(i)
sep += ' \t| --- '
print(header)
print(sep)
for i, result in enumerate(results):
name, result = results[i]
if result != None:
w = result[0]
line = '*' + name + '*'
for j in range(len(w)):
line += ' \t| ' + '{}'.format(round(w[j],5))
print(line)
else:
print('*' + name + '*',' \t| N/D '*len(initial_theta))